Starting a dairy farm in India
This post was initially prepared by Late Dr. P A Deore. Most of the information about dairy farming for prospective Indian entrepreneurs is available in this post. We have added some highly valued tips from experts. You can download bankable project reports and learn about legal requirements and details of government assistance schemes. The project report will give you an idea of the initial capital requirement and income from a dairy farm-based enterprise.
How safe is the dairy business?
Dairy farming is a safe business for the following reasons:
- It is eco-friendly and does not cause environmental pollution as compared to other industries.
- The requirement for skilled labor is relatively less.
- The dairy product market is active around the year.
- The minimum investment on inventory. (No need to stock raw materials in huge quantities.)
- The entire establishment can be shifted to a new location (if the need arises e.g. Fire, Floods, etc.)
- One can insure animals.
- Less energy requirement. Biogas plants fed with cow dung can supply maximum energy to meet farms day to day requirements. The decomposed slurry of such plants can also be effectively used as organic manure.
Limitations and Constraints:
- Breeding of animals and getting expected milk yield is a biological phenomenon, which depends upon various factors.
- Dairy farming besides good planning requires a hardworking, reliable, and alert manager. In India, usually, persons from the family take the responsibility.
- Inadequate management of feeding, herd health, and lack of quality control in various stages of production can cause major loss affecting the profitability of the entire venture.
Starting the Farm – How to begin with:
- One needs to decide first on the aims and objectives of the farm. Every year there should be a progressive aim for breeding (including the number of animals to be maintained) and production.
- You can visit dairy farms that run on a commercial basis and have a discussion with experienced farm owners. You need not have to rely much on others’ experience, analyze every event logically, and if needed consult with local Veterinarians for more information.
- If you plan to manage the farm on your own, look for opportunities to work for an existing farm for a minimum period of six months.
- Develop interest and study feed and fodder’s market in your region, its difficulties in relation to seasons.
- Manage a good team of laborers. You need to choose hardworking reliable persons preferably with some experience. You can also train them for specific jobs.
- Visit the cattle market occasionally. Observe animals on sale and talk with persons engaged with purchasing animals.
- Read magazines and websites on Dairy Industry and keep yourself informed.
Getting some initial professional training…
Opportunities for training are available with most of them:
- Agricultural/Veterinary Universities of various states
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras
- State Department of Animal Husbandry
- State Institute of Rural Development
You can also choose to inquire with a National level organization like National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI) Karnal (Haryana) – For training on the rearing of dairy animals and manufacture of milk products.
Alternately, you can also look for training facilities of non-governmental organizations that are active in the farming sectors.
![]() Selecting the animal to farm with – Cows v/s. Buffaloes
Selecting the animal to farm with – Cows v/s. Buffaloes
| Cows | Buffalo |
|
|
A suggestion to help you in deciding the animal to farm with:
Middle class health-conscious Indian families prefer low-fat milk for consumption as liquid milk. We suggest you go for a commercial farm of mixed type. (Crossbreed, cows, and buffaloes kept in separate rows under one shed). Conduct a thorough study of the immediate market where you are planning to market your milk. You can mix milk from both types of animals and sell as per the need of the market. Hotels and some general customers (can be around 30%) prefer pure buffalo milk. Hospitals, sanitariums prefer cow’s milk.
What are the various breeds? What is the economic life of animals?
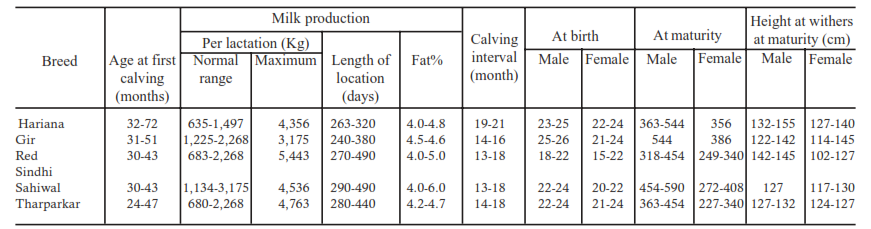
Popular buffalo milch breeds are Murrah, Surti, Mehasani, Jaffrabadi, and Nali – Ravi and Badhawari. The indigenous milch breeds of cattle are Gir, Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, and Tharparkar. The exotic breeds of cattle are Holstein Friesian, Jersey, and Brown Swiss.
The economic life of buffaloes is 5-6 lactation and that of Crossbreed cows is 6-7 lactation.
The minimum economic size to go with?
Under Indian conditions, a commercial dairy farm should consist of a minimum of 20 animals (10 cows, 10 buffaloes) this strength can easily go up to 100 animals in the proportion of 50:50 or 40:60. After this, however, you need to review your strength and market potential before you chose to go for expansion.
A glance at the Infrastructure and Manpower requirements
The space required per animal should be 40 sq. ft in shed and 80sq.ft open space. Besides, you will also need:
- One room 10” x 10” for keeping implements.
- One room 10”x 12” for milk storage
- Office cum living room of suitable size.
- Water tank capable of storing a minimum of 2000 liters
- Borewell with the capacity to fill the water tank in 1 hr
The total land requirement for a unit of 20 animals can be sited as 3000 sq. ft. There should be space for expansion. Ideal space requirement for 100 animals is 13,000 to 15,000 sq.ft (120″ x 125”). For 20 animals initially, you can make contractual arrangements for getting an assured supply of 300 kgs. of Lucerne and 400 kgs. of maize fodder per day. However, in long run, as the strength of your farm will go up to 100 animals, It is advisable that you should go for a lease land of 15 to 20 acres with an irrigation facility to cultivate green fodder for your animals. (One acre of green fodder cultivation for every five animals is required as a thumb rule.) The economics of whole dairy animal management depends upon its economic feeding. By making fodder like Lucerne or Berseem available for your animals you can reduce the cost of feeding concentrate feed.
The strength of laborers in your farm can vary with the number of animals usually the thumb rule is one labor for every 10 animals on milk or 20 dry animals or 20 young stock.
The legal requirement for setting up of dairy farm:
The legal requirement varies from state to state and whether you also intend to process milk ( Make milk products ). For a normal individual dairy farm, the first point of contact for registration ( mainly for the purpose of getting incentives,s, etc.) is the local veterinary and dairy development department ( Contact district/block office of these departments near your farm ). If your farm is a part of a registered dairy cooperative society, you are not required to approach any other government authority.
As far as the license is concerned, you need to contact veterinary or related officer of municipality corporation or local panchayat. For large farms, permission may be required from the pollution control board.
Click Here for the Central Pollution Control Board’s “Guidelines for Environmental Management of Dairy Farms and Gaushalas”.
You may like to follow various standards suggested by BIS (BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS) in connection with the dairy farms. For getting a copy of these standards check here
BIS IS 11799:1986 (R2002): Recommendations for Cattle Housing In Rural Areas
BIS IS 11942:1986 (R2002): Recommendations for Gaushalas and Other Organized Milk Producers
BIS IS 12237:1987 (Reaffirmed 2004): Recommendations for loose housing system for animals.
You can also download the draft Indian Standard Requirement for Good Agricultural Practices for the dairy sector dated 15th May 2011: India-GAP
If you are not a member of a cooperative society and intend to sell milk/milk products directly to consumers. A registration with FSSAI ( Food Safety and Standard Authority of India ) is mandatory. Click Here for a list of FSSAI offices in your state.
Tips from experts for prospective entrepreneurs:
Following tips are from Vet Helpline India’s experts:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the value of the land/property you intend to use for dairy farming. The opportunity cost of the land (i.e. potential earning if you use the land or property for other business –other than dairy ) and future value ( e.g. value of the land in next 5 years ) are important parameters for an informed decision regarding investment ( more particularly on fixed assets like housing etc.) in dairy farming. You also need to set aside some land for fodder cultivation (for 10 cows depending upon the soil, rainfall, irrigation facilities, land required varies but 1.5 – 2.0 acres). One should also assess personal expectations and try their best to understand the scale of operation vis a vis earning from dairy farming. Farming with live animals is a full-time operation and one need to sacrifice many things in life e.g. you cannot easily go for a holiday with family leaving your herd of animal to the supervision of a caretaker unless and until the caretaker is a skilled person and trustworthy. Similarly, like in other businesses, you cannot easily stop operations e.g. Feeding and milking are daily activities.
- Read available information on dairy farming ( including model bankable projects ) in India in general and your state in particular. It is always better to plan operations with fewer animals and expand with experience. One should note that high-yielding animals demand more care, proper nutrition, and a better environment in order to remain productive. Many farmers suffer huge loss when they purchase high yielders and fails to give required care, nutrition ( fodder and feed ), and environment ( e.g. housing, etc. )
- Visit any local dairy farm / cooperative dairy society / Self Help Group near the proposed location of your farm to take first-hand information about the business, more particularly about the source of good animal, suitable breed, Veterinary services, and market, etc. The selection of breed of animal can depend on the preference of the majority of successful farmers in your area. One should preferably buy animals from nearby known farms instead of from cattle markets. However, a visit to known cattle fair may be useful when animals are not available nearby or just to know the output of various breeds, available technology, and average prices. Visit our Facebook page to check updates on various cattle fairs. Keep newly purchased animals isolated for a few days for observation before mixing them with the existing herd. For any information pertaining to large farms, companies providing equipment, cattle feed, services to the dairy sector, etc. you can buy the Dairy India yearbook.
- Visit the local veterinary department office or Krishi Vigyan Kendra ( KVK ) or office of the state institute of rural development (SIRD ) or any large NGOs like Ram Krishna Mission in Kolkata to explore if they can help you with training, project formulation, bank linkage and insurance of animals, etc. The guideline and availability of these things vary from state to state in India.
- If your proposed farm falls under a milk cooperative or private milk processing unit, the officials of the concerned organization can help you with all aspects in setting up the farm with understanding that you will supply raw milk to them. In those areas where there are no cooperative or private dairy processing units, one can form self-help groups with other farmers, seek government help ( contact dairy development department of your state! ) for setting up milk cooling centers to aggregate milk from various farms, and collectively market the same to distant areas.
- We strongly recommend for one to decide on dairy farming only in such localities where there are other farms and quality support systems e.g. Suppliers of inputs, veterinary facilities, marketing arrangements,s, etc. are in place. Otherwise, you can talk to some of your neighbors and encourage them to for dairy farming. More production in any locality will attract service providers and milk quantity too will be sufficient for marketing in distant areas or value-added processing.
- Prepare the project report ( you may take the help of bank suggested consultants ! Ask your bank manager for reference. ) and approach nationalized banks for financial assistance with government subsidy under Venture capital and other schemes. Note that NABARD bank only refinance i.e. you have to approach a nationalized bank who in turn will determine your eligibility for assistance under the NABARD scheme. Generally credit limit depends on your own financial standing and feasibility of the project in the chosen location. Your bank is the best organization to guide you on this. Always communicate with the bank through appropriate channels and keep a record of these communications. A scheduled bank should not refuse your application without giving due details in writing regarding the ground for refusal. You can further refer following websites for model project reports and subsidy details: OdishaVet.Com and Download Project Report.Com
- The project report is the most important document for you and it is advisable that you understand the report thoroughly. Planning, record keeping, and mid-course correction ( if required ) are essential.
- Ask any local veterinarian of the concerned district or dairy farm consultant associated with the local bank for his service such as guidance to design the farm site, select good animals for purchase, plan for fodder cultivation, etc. There are innovative ways to go for less costly but comfortable animal housing. In some parts of the country, a loose housing system has recently gained much popularity as same is less costly, environmentally friendly, and gives better productivity too. You can visit this resource1 and resource2 to learn more. Do check our Facebook page for other housing and management-related postings.
- Fodder production is another important area. Contract fodder production in farmers’ fields during the time between wheat and rice cultivation and making silage is the best option if own land is not available. You can also grow your own Green Fodder… the Hydroponic way. You can search google for references and practical examples.
- Once you established the farm with the first set of purchased animals, a good breeding program to efficiently manage and expand your initial herd of animals is essential for productivity. Artificial insemination is a tested technique whereby you can design a breeding program without male animals. Many state governments in India are promoting artificial insemination ( AI ) and supply ‘semen’ to farmers at nominal cost. Animal Health workers and veterinarians can help you inseminate animals when they are on heat. If you are interested in getting the best animal through the planned breeding program, you can also go for imported semen. Note nowadays even sexed semen ( use of sexed semen will ensure only female calf) is also available.ABS Global (USA) and is one of the largest sellers of imported semen in India.
- As far as the day-to-day running of the farm is concerned, there are also numerous books and websites which can guide you on specific topics like feeding, dry period management, etc. You can check open-source resources like expert systems for cattle and buffaloes. A formal training covers most of the day-to-day management aspects. A good formal training source is Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University: Alternatively, you can apply for the IGNOU distance learning course: “Awareness Programme on Dairy Farming for Rural Farmers (APDF): You can also download the National occupational standard of the dairy entrepreneur in India.
- Many farmers want to start an organic dairy farms. Getting formal certification for the organic farm is a long process and needs investments. The cost of production of organic certified milk is high and therefore you need to survey your market to understand the price premium for organic milk in your area. To learn more about organic certification of milk you can contact: One Cert Asia and visit resources like Information System for Organic Livestock Farming in India. Near organic milk ( not certified ) production is always encouraged but everything will depend on economics i.e. the price of milk you will get. Note for organic milk production you need to feed your cattle with feed and fodder which is free of any chemicals. Getting such inputs is a challenge.
- Nowadays, there are Indian companies that can help you keep scientific farm-level data on a web-based platform and do the analysis of such data for preventive and management-related actions. This is very important as prevention of diseases in Animals is always better than cure and progress of the farm cannot be measured without proper data recording. Such service providers give you pre-warning or alert SMSs. You can upload data e.g. milk production record, breeding record, treatment record, etc. using your mobile phone and receive reports via SMS. Visit this link to learn more.
- ‘Dairy farming’ and ‘milk processing’ are two related but different activities. Processing is possible both in small scale ( traditional ) and in ‘medium to large’( with equipment ) scale. To learn more about small-scale processing you can read: FAO Resource and ILRI Resources. Some of the known companies that supply milk processing equipment etc. are Alfa Laval, SSP Private Limited, etc. Medium to large scale milk processing is a high investment business and one needs to either produce a large quantity of milk ( generally min 3000 lit milk ) or procure milk from small farmers. Milk procurement, processing, and marketing of products is a competitive business activity and requires detailed planning. In India nowadays very large companies like ITC, Reliance, etc. are now entering into the milk processing business, and in the years to come more Indian and foreign companies are likely to come up with numerous dairy products.
- Please note that dairy farming can be also integrated with other livestock, poultry, and agriculture farming. To know more about the concept of integrated farming check: http://www.fao.org/docrep/x5686e/x5686e07.htm
If you want to invest in large projects, we advise you to contact any known consultant. Banks are also usually good reference points for locating consultants. Another way is to look for personal references from existing large farms in your area. The usual charges for consultancy in India are 1-5% of project cost but may vary depending on project size, area, scope, etc. Many consultants ask for fees for answering queries over the phone. It is always better to sign an annual retention contract with a select consultant to assist over the phone ( if not in person ) in the initial years ( Before you train yourself or your employees ).

Click Here to visit the Centre of Excellence for Dairy Skills in India (CEDSI) -An autonomous institution committed to dairy skill development in India,
The consultant who has worked with Vet Helpline India Pvt Ltd and its sister concerns like FARMER:
Captain (Dr.) Kiran Konher
Address:604 Gaurang, Prasun Dham,
Survey No. 32, Thergaon Opposite Aditya Birla Hospital, Chinchwad
Pune – 411033, Maharashtra (India)
Phone :+(91)-(20)- 32902383 / 27308057 (8:00AM to 1:00PM & 4:30PM to 8:30PM IST on weekdays)
E-mail: dairyassist@gmail.com
Click the relevant links to download:
Do ‘Like’ our Facebook page for regular updates: Click Here
National Occupational Standard for Dairy Farmer / Entrepreneur





[…] ↑http://www.vethelplineindia.co.in/starting-a-dairy-farm-india/ […]